Apple trees grow in stages, starting with planting young saplings, developing roots, and then branching and leafing. They bloom, forming small apples that mature over weeks to months. Harvested when ripe, they repeat the annual cycle—growth, flowering, fruiting, and dormancy—with care for consistent fruit production and healthy trees.
How tall do apple trees grow?
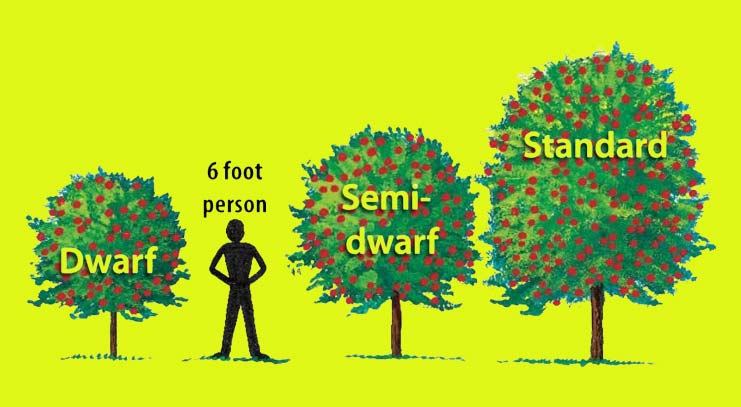
The ultimate height of apple trees grow can vary based on factors like the apple variety, rootstock, and local growing conditions. Standard apple trees, if left unpruned, typically reach heights ranging from 15 to 30 feet (4.5 to 9 meters). However, many gardeners prefer to maintain smaller, more manageable tree sizes by regular pruning and selecting dwarf or semi-dwarf rootstocks. Semi-dwarf apple trees usually grow to about 10-15 feet (3-4.5 meters), while dwarf varieties may reach heights of 6-10 feet (1.8-3 meters). These smaller sizes make maintenance, harvesting, and pest/disease management more accessible for home gardeners while still yielding a respectable crop of delicious apples.
Generally, apple trees can be categorized into three main types based on their expected height: dwarf, semi-dwarf, and standard. Described below:
Dwarf Apple Tree Height:

Advantages of Dwarf Apple Trees:
- Space Efficiency: Dwarf apple trees are well-suited for small gardens and limited spaces, as they take up less room than standard-sized apple trees.
- Early Fruit Production: Dwarf varieties typically begin bearing fruit at a younger age than full-sized trees, often within 2 to 3 years after planting.
- Ease of Maintenance: Their smaller size makes pruning, thinning, and overall care more accessible, reducing the need for ladders and special equipment.
- Convenient Harvest: The fruit is within easy reach, simplifying the harvest process and reducing the risk of fruit damage during picking.
- Variety Selection: Many apple varieties are available in dwarf forms, allowing for a diverse range of apple types and flavors in a limited space.
- Customizable Growth: Rootstock selection allows you to control the size of the tree to fit your available space and desired tree height.
- Improved Pest and Disease Management: Smaller canopies make it easier to inspect for pests and diseases and apply treatments, contributing to tree health.
Disadvantages of Dwarf Apple Trees:
- Reduced Longevity: Dwarf apple trees typically have a shorter lifespan compared to standard-sized trees, often requiring more frequent replanting.
- Potentially Lower Yield: While they may bear fruit earlier, dwarf trees might produce fewer apples per tree than larger varieties.
- Rootstock Compatibility: Proper rootstock selection is crucial, and compatibility issues can lead to poor growth or reduced lifespan.
- Special Care Required: Dwarf trees may need more attention to soil quality, watering, and fertilization to ensure healthy growth and productivity.
- Pollination Requirements: Some dwarf apple varieties require cross-pollination from another apple tree to set fruit, necessitating the planting of compatible varieties nearby.
- Susceptibility to Tipping: Due to their compact size, dwarf trees may be more prone to tipping over in strong winds or heavy fruit loads unless adequately supported.
- Limited Reach: The lower height of dwarf trees may require bending or squatting during maintenance and harvesting, which can be uncomfortable for some individuals.
Semi-Dwarf Apple Tree Height:
Advantages of Semi-Dwarf Apple Trees:
- Moderate Size: Semi-dwarf apple trees are smaller and more manageable than standard-sized trees, making them easier to prune, harvest, and maintain.
- Faster Fruit Production: They typically start bearing fruit earlier than standard trees, often within 2 to 4 years after planting, allowing for quicker enjoyment of homegrown apples.
- Improved Disease Resistance: Semi-dwarf varieties can have better disease resistance compared to dwarf trees, reducing the need for chemical treatments in orchards.
- Adaptability: They can be grown in various soil types and climates, making them versatile for a range of growing conditions.
- Variety Selection: Many apple varieties are available in semi-dwarf forms, allowing growers to choose from a wide array of flavors and characteristics.
- Customizable Growth: Rootstock selection still plays a role in controlling the size of semi-dwarf trees, allowing for some flexibility in tree height.
Disadvantages of Semi-Dwarf Apple Trees:
- Space Requirement: Semi-dwarf apple trees are larger than dwarf varieties, requiring more space in orchards and gardens.
- Longer to Maturity: While they bear fruit earlier than standard trees, semi-dwarf varieties may take longer to reach full maturity compared to dwarfs.
- Not Ideal for Very Small Spaces: For extremely limited spaces, even semi-dwarf trees might be too large, necessitating alternative options like dwarf or espaliered trees.
- Rootstock Selection Complexity: Proper rootstock selection is critical to control growth. Inappropriate choices can result in trees that are too large or too small for the intended space.
- Maintenance Requirements: Semi-dwarf trees still require regular maintenance, including pruning and pest management, to ensure optimal growth and fruit production.
Standard Apple Trees Height:

Advantages of Standard Apple Trees:
- High Fruit Yield: Standard apple trees typically produce a substantial quantity of fruit per tree, making them ideal for commercial orchards and large-scale fruit production.
- Longevity: They have a longer lifespan compared to dwarf and semi-dwarf trees, providing consistent fruit production for many years.
- Tall Canopy: Their larger canopy can provide shade in the garden or orchard, creating a more significant impact on the landscape.
- Resilience: Standard trees often have more extensive root systems, making them more resilient in adverse weather conditions and less prone to tipping over.
- Variety Selection: A wide range of apple varieties is available in standard sizes, offering diverse flavor profiles and characteristics for growers to choose from.
Disadvantages of Standard Apple Trees:
- Space Requirements: Standard apple trees require substantial space, making them unsuitable for small gardens or limited urban areas.
- Slower to Fruit: They generally take longer to begin bearing fruit compared to dwarf and semi-dwarf trees, often requiring 4 to 6 years or more.
- Challenging Maintenance: Pruning, harvesting, and overall tree care can be more challenging due to their height and size, often necessitating ladders or special equipment.
- Increased Disease Risk: Their larger canopies can create a more favorable environment for certain diseases, requiring more extensive pest and disease management.
- Resource Intensive: Standard trees may require more water, nutrients, and space than smaller varieties, which can be less environmentally friendly and resource-intensive.
Finally, proper care is essential for apple trees to grow tall.

